Cooperative Perception of Road-Side Unit and Onboard Equipment with Edge Artificial Intelligence for Driving Assistance
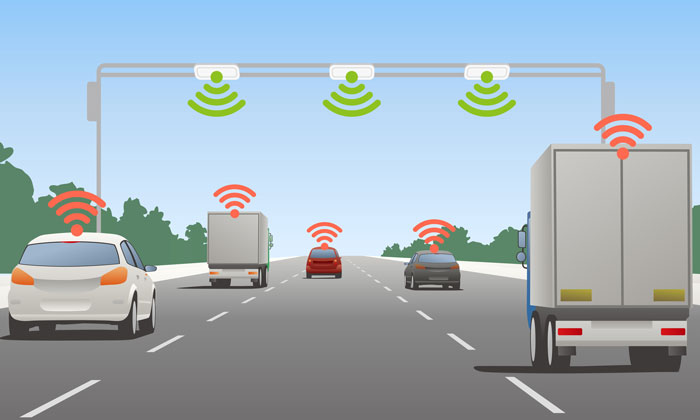
Although lots of research have been conducted on multi-vehicle cooperative perception, few studies have considered combining information from vehicle onboard sensors and roadside sensors. This project argues that it would be highly beneficial to utilize roadside sensors for cooperative driving perception.