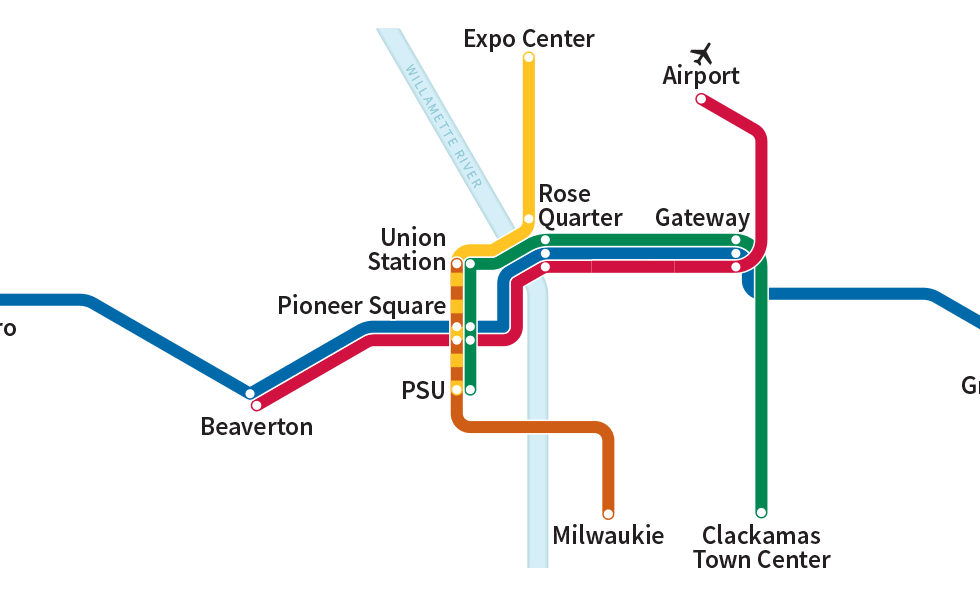
The cost to build and operate transportation infrastructure, including mass transit, in the United States is consistently higher than it is elsewhere in the developed world. As America’s population becomes increasing urban, addressing this issue will become increasingly important. This study seeks to understand why this cost discrepancy exists, and what to do about it, through a review of existing cost data (using operations costs from the US and International governments, and capital cost data from prior studies) and a comparative case study analysis. Two light rail systems, MAX (in Portland, Oregon) and Metrolink (in Manchester, UK), share many design and operations characteristics, and recently completed two similar capital projects. While MAX’s operations and capital costs are lower than the national average, they remain above comparable costs for Metrolink. This similarity in specifications, combined with a divergence in cost, provides an opportunity to understand why US transit is comparatively expensive.