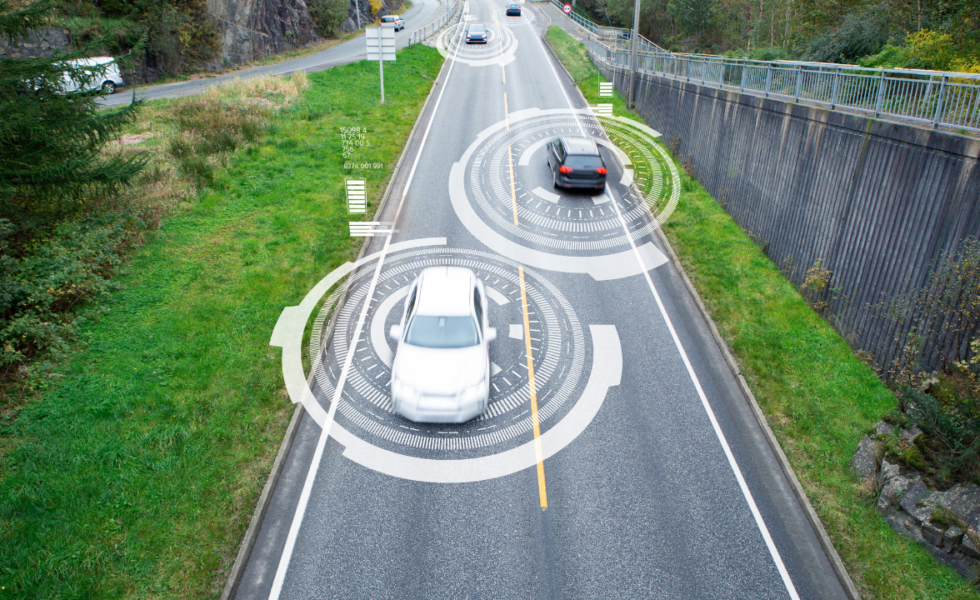
Blockchain for Preserving Privacy in V2X Connected Vehicle Applications in Urban Environments
C2SMART researchers developed a more efficient, secure, blockchain-based system to story mobility data on a distribute ledger. To store this data at scale, researchers leverage InterPlanetary File System (OPFS), a scalable distributed peer-to-peer data storage system, and develop efficient consensus algorithms to prevent users from injecting malicious or fake trajectories into the ledger.